























Apr 18, 2023

Data is the lifeblood of modern organizations, informing critical decision-making, powering analytics, and driving innovation. But with the proliferation of data usage from various sources, organizations need robust data management and governance practices.
One key aspect of effective data management is understanding data lineage, which tracks the data journey from its origin to its current state and all the transformations it undergoes along the way.
Want to implement an agile data governance program at your organization? Read this playbook to understand the fundamentals as you transition from top-down governance.
Data lineage — also referred to as data provenance — is the tracking of data as it flows through various data systems, applications, and processes.
Data lineage tools provide a comprehensive view of the end-to-end movement of data elements, including their sources, transformations, and destinations. Data lineage tools capture information such as data sources, data transformations, data migrations, data dependencies, and data values, allowing organizations to understand data flow, and how data changes as it moves within their data environment.

Data lineage is invaluable to data teams and data-driven organizations in general. It plays a significant role in:
Data Quality:
Data lineage provides visibility into the data flow and transformations, enabling data engineers and data scientists to trace data errors and identify data quality issues. By understanding data lineage, organizations can identify and rectify data quality issues at their source, ensuring that downstream data consumers are working with accurate and reliable data.
Data lineage becomes particularly important in ensuring data quality within complex data environments — e.g. big data environments and cloud computing — where data moves across myriad different systems and undergoes numerous transformations.
The visibility provided by data lineage also promotes trust in your organization's data. For example, if a data scientist finds a BI dashboard that they can use to answer a critical business question, she may not be sure if she can trust the data. But by looking at the lineage of the data feeding the BI dashboard, she can see that the data comes from an approved data source and can reach out to the appropriate data steward with any questions.
Impact Analysis:
Lineage helps organizations assess the impact of changes to data sources, transformations, or destinations. It allows data engineers and data scientists to understand how changes in one part of the data pipeline can impact downstream data assets, applications, and processes. This helps organizations make informed decisions about changes to data systems or data assets, minimizing potential disruptions and ensuring smooth data operations.
For example, if a data engineer is tasked with adding new assets to a data warehouse, it may result in moving columns to another table. If so, what will break downstream? And who should be informed? Data lineage can answer these questions.
Data Discovery:
Data lineage provides a comprehensive view of data sources, transformations, and destinations, making it easier for organizations to discover relevant data for their business processes or analytical needs. It enables data analysts and data scientists to understand the data flow and lineage of data assets, making it easier to identify relevant data sets for their analysis or modeling purposes.
Data Management:
Data lineage plays a critical role in data management, helping organizations manage data assets, data flows, and data systems effectively. It provides insights into data movements, data transformations, and data dependencies, allowing businesses to optimize their data pipelines, manage data integrations, and ensure efficient data processing across their data environment.
Data Lifecycle Management:
Lineage supports data lifecycle management, which encompasses the various stages of data from creation to deletion. By understanding data lineage, organizations can track data through its entire lifecycle, ensuring proper data handling, data retention, and data deletion practices. This helps organizations comply with data regulations and manage data assets effectively.
Data Asset Management:
Data lineage helps organizations manage data assets, valuable resources that organizations use to derive insights, make decisions, and drive business outcomes. By understanding the lineage of data assets, organizations can track data assets, manage data asset dependencies, and ensure proper data asset documentation
Implementing data lineage involves capturing, tracking, and documenting the movement of data across your organization's data systems. It typically includes the following steps:
Data Discovery:
Identifying and cataloging all relevant data sources and data sets within the organization's data environment, including structured and unstructured data in your data warehouse, data lake, operational systems, and cloud-based data sources.
Data Tagging:
Assigning metadata tags to data elements, such as data source, data type, data owner, and data classification. This helps in identifying sensitive data, relevant data, and data dependencies during the data lineage process.
Data Lineage Tracking:
Capturing data lineage information as data moves through various data flows, data transformations, and data assets. This includes recording the source and destination of data, the processes it goes through, and any data transformations applied to it.
Data Lineage Documentation:
Creating comprehensive documentation that captures the data lineage information in a standardized and easily understandable format. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for data engineers, data scientists, and business users to understand and analyze the movement of data across the organization's data systems.
Want to implement an agile data governance program at your organization? Read this playbook to understand the fundamentals as you transition from top-down governance.

Data lineage is a critical component of data governance initiatives, as it helps organizations understand the origins and transformations within a data system, promotes transparency and understanding of data relationships, and ensures data is used appropriately and in compliance with relevant data regulations and policies.
This helps businesses meet compliance requirements, trace data breaches, and manage data-related risks effectively. It also enables organizations to establish data standards, define data ownership, trace errors, and track changes from start to finish in their data flow.
Data lineage tools built into a data catalog benefit a wide range of users: they to address the high-level needs of business analysts, data stewards, project managers, executives, and stakeholders while positively impacting deeper troubleshooting and complex analyses performed by more specialized roles, such as IT leaders and data engineers.
(In this webinar, you can see how data lineage contributes to bridging the gap between technical and business users.)
Above, we introduced the two most-common types of data lineage, technical data lineage and business data lineage.
Less commonly discussed, but nevertheless important, is the semantic layer that connects the two.
In and of itself, data has little value. It’s the knowledge that can be gleaned from your data that’s worth its weight in gold. And that’s why it’s crucial to build a semantic layer a — layer of knowledge — that consists of the key business concepts within your organization and the relationships between them.
The semantic layer should live in your data catalog because that is where it’s defined, explained, and mapped to the source data. It uses common business language to empower your non-technical workers to find the data they need, understand what data they’re looking at, and how it relates to all facets of your organization.
But here's the kicker: when it comes to bridging your technical data to your business concepts, only a data lineage solution powered by a knowledge graph provides insight into the relationships between the two to create truly meaningful, useful business data lineage.
The same foundation that companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Google use to deliver automation, discovery, and context to their customers, knowledge graphs are inherently semantic. Each one has an ontology which serves to create a formal representation of the entities in the graph and explain how they’re related.
In short, it tells you what everything in your data means, making it easier to understand how that data is connected.

And the benefits of knowledge graph data lineage don’t stop there. Inferencing – the ability to discover new relationships in your data based on related information stored in disparate sources – helps overcome incomplete or contradictory information, while PROV-O – an open standard for describing Provenance in RDF – can be used to form assessments about data’s quality, reliability, or trustworthiness. PROV-O also allows you to build your own concepts into data lineage, enabling you to expand tracking beyond traditional data and analytics environments.
These capabilities are essential for operationalizing your data lineage and delivering on the promise of faster, more efficient data-driven decision making.
Unfortunately, most catalog-native data lineage solutions struggle to interrelate data lineage with essential business concepts.
Ours is different.
data.world's data catalog is built on a knowledge graph, which enhances data governance efforts by mapping data assets to key enterprise concepts, interrelating data lineage with essential business concepts to make them easily discoverable and accessible for greater user self service.
This semantic relevance is something only a knowledge graph can provide.
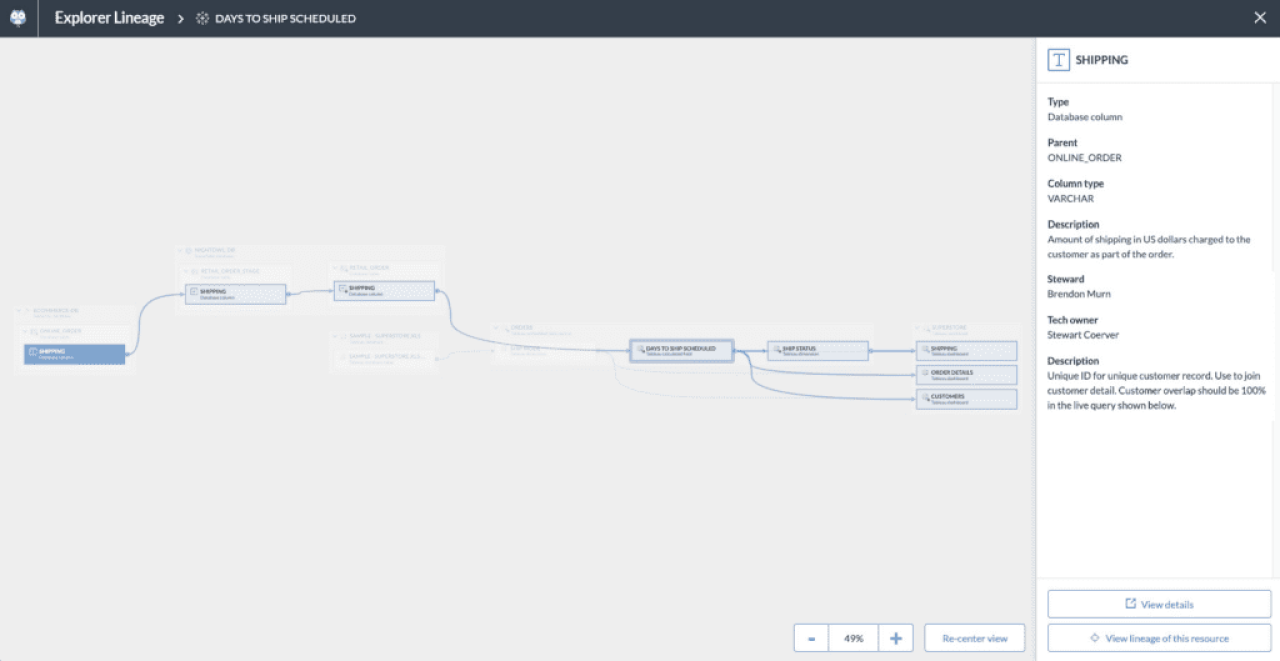
Enter Eureka™ Explorer Lineage is a an automated column-level technical data lineage tool powered by data.world’s knowledge graph.
Explorer Lineage enables all members of an organization’s data team to make data-driven decisions faster with full visibility into the modern data stack.
With an easy-to-follow, visual, and interactive user interface, Explorer Lineage can show where data is sourced, how it’s aggregated, and any transformations it undergoes along its journey.
data.world’s Explorer Lineage leverages context from the knowledge graph to visually map data to familiar business terms, delivering a unified, consolidated view of data to the entire organization. The knowledge graph enables data lineage to be queried in order to answer any type of question and serves as a source of truth, providing valuable insight into your most important data assets.
Explorer Lineage gives your organization visibility into its data flow with complete context, providing knowledge, meaning, and visibility that helps ensure accurate, complete, and trustworthy data is being used to drive your business forward.
Data lineage tools enable teams to achieve a comprehensive view of data relationships, providing transparency and data insight that improves governance, confidence, impact and root-cause analyses, troubleshooting, forecasting initiatives, and more.
data.world's Eureka™ Explorer Lineage visual data lineage tool shows where data is sourced, how it’s aggregated, and any transformations it undergoes along its journey, empowering all members of your organization’s data team to make data-driven decisions faster and with total confidence in their information sources.
Learn how Eureka™ Explorer Lineage provides an easy and automated top-down view of your data and analytics ecosystems.

Data is the lifeblood of modern organizations, informing critical decision-making, powering analytics, and driving innovation. But with the proliferation of data usage from various sources, organizations need robust data management and governance practices.
One key aspect of effective data management is understanding data lineage, which tracks the data journey from its origin to its current state and all the transformations it undergoes along the way.
Want to implement an agile data governance program at your organization? Read this playbook to understand the fundamentals as you transition from top-down governance.
Data lineage — also referred to as data provenance — is the tracking of data as it flows through various data systems, applications, and processes.
Data lineage tools provide a comprehensive view of the end-to-end movement of data elements, including their sources, transformations, and destinations. Data lineage tools capture information such as data sources, data transformations, data migrations, data dependencies, and data values, allowing organizations to understand data flow, and how data changes as it moves within their data environment.

Data lineage is invaluable to data teams and data-driven organizations in general. It plays a significant role in:
Data Quality:
Data lineage provides visibility into the data flow and transformations, enabling data engineers and data scientists to trace data errors and identify data quality issues. By understanding data lineage, organizations can identify and rectify data quality issues at their source, ensuring that downstream data consumers are working with accurate and reliable data.
Data lineage becomes particularly important in ensuring data quality within complex data environments — e.g. big data environments and cloud computing — where data moves across myriad different systems and undergoes numerous transformations.
The visibility provided by data lineage also promotes trust in your organization's data. For example, if a data scientist finds a BI dashboard that they can use to answer a critical business question, she may not be sure if she can trust the data. But by looking at the lineage of the data feeding the BI dashboard, she can see that the data comes from an approved data source and can reach out to the appropriate data steward with any questions.
Impact Analysis:
Lineage helps organizations assess the impact of changes to data sources, transformations, or destinations. It allows data engineers and data scientists to understand how changes in one part of the data pipeline can impact downstream data assets, applications, and processes. This helps organizations make informed decisions about changes to data systems or data assets, minimizing potential disruptions and ensuring smooth data operations.
For example, if a data engineer is tasked with adding new assets to a data warehouse, it may result in moving columns to another table. If so, what will break downstream? And who should be informed? Data lineage can answer these questions.

Data Discovery:
Data lineage provides a comprehensive view of data sources, transformations, and destinations, making it easier for organizations to discover relevant data for their business processes or analytical needs. It enables data analysts and data scientists to understand the data flow and lineage of data assets, making it easier to identify relevant data sets for their analysis or modeling purposes.
Data Management:
Data lineage plays a critical role in data management, helping organizations manage data assets, data flows, and data systems effectively. It provides insights into data movements, data transformations, and data dependencies, allowing businesses to optimize their data pipelines, manage data integrations, and ensure efficient data processing across their data environment.
Data Lifecycle Management:
Lineage supports data lifecycle management, which encompasses the various stages of data from creation to deletion. By understanding data lineage, organizations can track data through its entire lifecycle, ensuring proper data handling, data retention, and data deletion practices. This helps organizations comply with data regulations and manage data assets effectively.
Data Asset Management:
Data lineage helps organizations manage data assets, valuable resources that organizations use to derive insights, make decisions, and drive business outcomes. By understanding the lineage of data assets, organizations can track data assets, manage data asset dependencies, and ensure proper data asset documentation
Implementing data lineage involves capturing, tracking, and documenting the movement of data across your organization's data systems. It typically includes the following steps:
Data Discovery:
Identifying and cataloging all relevant data sources and data sets within the organization's data environment, including structured and unstructured data in your data warehouse, data lake, operational systems, and cloud-based data sources.
Data Tagging:
Assigning metadata tags to data elements, such as data source, data type, data owner, and data classification. This helps in identifying sensitive data, relevant data, and data dependencies during the data lineage process.
Data Lineage Tracking:
Capturing data lineage information as data moves through various data flows, data transformations, and data assets. This includes recording the source and destination of data, the processes it goes through, and any data transformations applied to it.
Data Lineage Documentation:
Creating comprehensive documentation that captures the data lineage information in a standardized and easily understandable format. This documentation serves as a valuable resource for data engineers, data scientists, and business users to understand and analyze the movement of data across the organization's data systems.
Want to implement an agile data governance program at your organization? Read this playbook to understand the fundamentals as you transition from top-down governance.

Data lineage is a critical component of data governance initiatives, as it helps organizations understand the origins and transformations within a data system, promotes transparency and understanding of data relationships, and ensures data is used appropriately and in compliance with relevant data regulations and policies.
This helps businesses meet compliance requirements, trace data breaches, and manage data-related risks effectively. It also enables organizations to establish data standards, define data ownership, trace errors, and track changes from start to finish in their data flow.
Data lineage tools built into a data catalog benefit a wide range of users: they to address the high-level needs of business analysts, data stewards, project managers, executives, and stakeholders while positively impacting deeper troubleshooting and complex analyses performed by more specialized roles, such as IT leaders and data engineers.
(In this webinar, you can see how data lineage contributes to bridging the gap between technical and business users.)
Above, we introduced the two most-common types of data lineage, technical data lineage and business data lineage.
Less commonly discussed, but nevertheless important, is the semantic layer that connects the two.
In and of itself, data has little value. It’s the knowledge that can be gleaned from your data that’s worth its weight in gold. And that’s why it’s crucial to build a semantic layer a — layer of knowledge — that consists of the key business concepts within your organization and the relationships between them.
The semantic layer should live in your data catalog because that is where it’s defined, explained, and mapped to the source data. It uses common business language to empower your non-technical workers to find the data they need, understand what data they’re looking at, and how it relates to all facets of your organization.
But here's the kicker: when it comes to bridging your technical data to your business concepts, only a data lineage solution powered by a knowledge graph provides insight into the relationships between the two to create truly meaningful, useful business data lineage.
The same foundation that companies like Netflix, Amazon, and Google use to deliver automation, discovery, and context to their customers, knowledge graphs are inherently semantic. Each one has an ontology which serves to create a formal representation of the entities in the graph and explain how they’re related.
In short, it tells you what everything in your data means, making it easier to understand how that data is connected.

And the benefits of knowledge graph data lineage don’t stop there. Inferencing – the ability to discover new relationships in your data based on related information stored in disparate sources – helps overcome incomplete or contradictory information, while PROV-O – an open standard for describing Provenance in RDF – can be used to form assessments about data’s quality, reliability, or trustworthiness. PROV-O also allows you to build your own concepts into data lineage, enabling you to expand tracking beyond traditional data and analytics environments.
These capabilities are essential for operationalizing your data lineage and delivering on the promise of faster, more efficient data-driven decision making.
Unfortunately, most catalog-native data lineage solutions struggle to interrelate data lineage with essential business concepts.
Ours is different.
data.world's data catalog is built on a knowledge graph, which enhances data governance efforts by mapping data assets to key enterprise concepts, interrelating data lineage with essential business concepts to make them easily discoverable and accessible for greater user self service.
This semantic relevance is something only a knowledge graph can provide.
Enter Eureka™ Explorer Lineage is a an automated column-level technical data lineage tool powered by data.world’s knowledge graph.
Explorer Lineage enables all members of an organization’s data team to make data-driven decisions faster with full visibility into the modern data stack.
With an easy-to-follow, visual, and interactive user interface, Explorer Lineage can show where data is sourced, how it’s aggregated, and any transformations it undergoes along its journey.
data.world’s Explorer Lineage leverages context from the knowledge graph to visually map data to familiar business terms, delivering a unified, consolidated view of data to the entire organization. The knowledge graph enables data lineage to be queried in order to answer any type of question and serves as a source of truth, providing valuable insight into your most important data assets.
Explorer Lineage gives your organization visibility into its data flow with complete context, providing knowledge, meaning, and visibility that helps ensure accurate, complete, and trustworthy data is being used to drive your business forward.
Data lineage tools enable teams to achieve a comprehensive view of data relationships, providing transparency and data insight that improves governance, confidence, impact and root-cause analyses, troubleshooting, forecasting initiatives, and more.
data.world's Eureka™ Explorer Lineage visual data lineage tool shows where data is sourced, how it’s aggregated, and any transformations it undergoes along its journey, empowering all members of your organization’s data team to make data-driven decisions faster and with total confidence in their information sources.
Learn how Eureka™ Explorer Lineage provides an easy and automated top-down view of your data and analytics ecosystems.
Get the best practices, insights, upcoming events & learn about data.world products.