







Jul 01, 2020
Thaise Skogstad

The easiest way to understand data lineage is to think about how data transforms itself during any type of process. As an example, think about retail transactions that may turn into warranty claims due to defective merchandise. Records such as transaction and warranty start dates may have been manually revised due to several factors, impacting the results of a particular warranty claim. Data lineage offers a comprehensive view of data relationships. It provides confidence and transparency to accurately respond to this specific claim, ensuring customer satisfaction without jeopardizing the retail store’s profitability goals.
Data lineage tracks the record of changes and transformations impacting any data record. It states where data is coming from, where it is going, and what happens to it as it flows from data sources and ETL workflows to downstream data marts and dashboards.
Data lineage capabilities in a data catalog benefit a wide range of users: it helps to address the high-level needs of business analysts, data stewards, project managers, executives, and stakeholders while positively impacting deeper troubleshooting and complex analyses performed by more specialized roles, such as IT leaders and data engineers. Check out this webinar, you’ll see how data lineage contributes to bridging the gap between technical and business users.
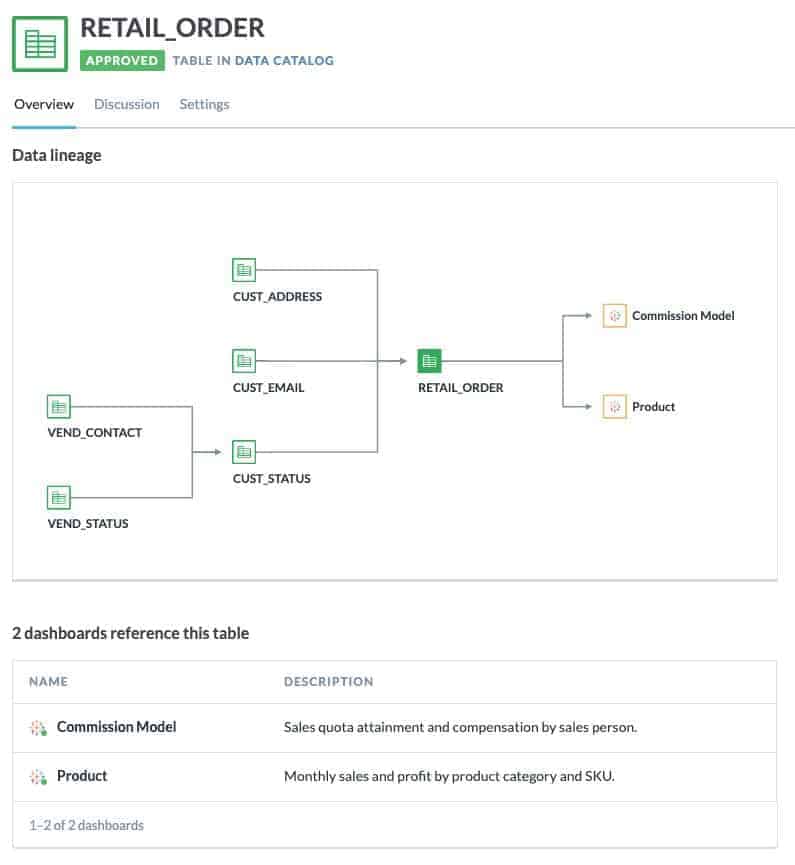
High-level visualizations: displayed in context for clear relationship to the information asset. It combines information on sources, transformations, and destinations.
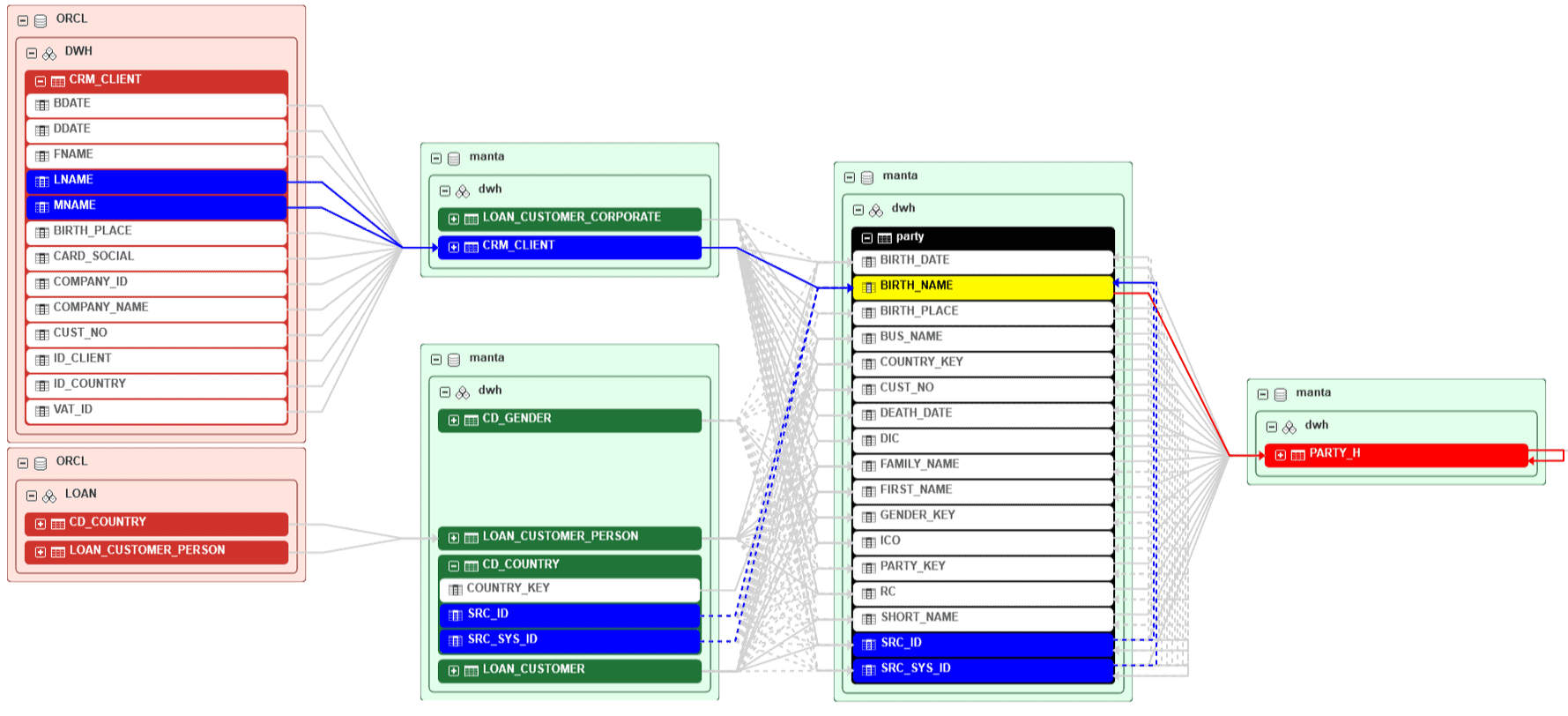
Technical lineage visualizations: used by developers, IT, security, and tech-savvy data analysts. It provides analyses of ETL workflows, database stored procedures, etc.
Data lineage is essential to organizations because it ensures transparency and understanding of data relationships, avoiding data quality deterioration while enabling businesses to adhere to industry regulations and standards. Here are its most popular use cases:
Source and Provenance: demonstrates where data originated and delivers an understanding of source/upstream systems, assets, and processes leading to a particular asset for context, trust, and troubleshooting. For example, a data scientist finds a BI dashboard that they can use to answer a critical business question, but they may not be sure if they can trust the data. By looking at the lineage of the data feeding the BI dashboard, the business user can see that the data comes from an approved data source and can reach out to the data steward if they have more questions.
Impact Analysis and Forecasting: drives business decisions as it maps the progress of data pipelines within a certain environment. It provides an understanding of the dependent/downstream systems, assets, and processes derived from a particular asset for context and determining the effect of potential changes. For example, a data engineer is tasked to add new data into a warehouse which may result in moving columns to another table? What will break? Who should be informed? Data lineage can answer these questions.
Troubleshooting and Root Cause: pinpoints the stage in the data pipeline where an error may have occurred. It allows the understanding of why a downstream dashboard or data mart is behaving unexpectedly or broken by tracing the source of the information and any applicable transformations. For example, a data analyst is skeptical about the data coming from a particular column. With data lineage, the business user can track the logic defined in a data transformation that occurred in an ETL pipeline that generated the data, in order to confirm if the data is accurate.
Risk and Sensitive Data: Assure compliance with industry regulatory frameworks (like GDPR and CCPA) by understanding how sensitive information such as PII is being utilized throughout data pipelines from their sources to reports and dashboards. For example, a data steward needs to track which data sources are providing email.
Metadata management systems featuring data lineage enable teams to achieve a comprehensive view of data relationships. This level of granularity provides transparency and confidence to organizations, ultimately improving governance, impact and root-cause analyses, troubleshooting, and forecasting initiatives.
We took a closer look at data lineage and how it integrates with your enterprise data catalog during our weekly data podcast, Catalog & Cocktails. Special guest Ernie Ostic from our partner, MANTA, joined us for the discussion. Listen to the episode now, and register for Catalog & Cocktails to join us every week.

The easiest way to understand data lineage is to think about how data transforms itself during any type of process. As an example, think about retail transactions that may turn into warranty claims due to defective merchandise. Records such as transaction and warranty start dates may have been manually revised due to several factors, impacting the results of a particular warranty claim. Data lineage offers a comprehensive view of data relationships. It provides confidence and transparency to accurately respond to this specific claim, ensuring customer satisfaction without jeopardizing the retail store’s profitability goals.
Data lineage tracks the record of changes and transformations impacting any data record. It states where data is coming from, where it is going, and what happens to it as it flows from data sources and ETL workflows to downstream data marts and dashboards.
Data lineage capabilities in a data catalog benefit a wide range of users: it helps to address the high-level needs of business analysts, data stewards, project managers, executives, and stakeholders while positively impacting deeper troubleshooting and complex analyses performed by more specialized roles, such as IT leaders and data engineers. Check out this webinar, you’ll see how data lineage contributes to bridging the gap between technical and business users.

High-level visualizations: displayed in context for clear relationship to the information asset. It combines information on sources, transformations, and destinations.
Technical lineage visualizations: used by developers, IT, security, and tech-savvy data analysts. It provides analyses of ETL workflows, database stored procedures, etc.

Data lineage is essential to organizations because it ensures transparency and understanding of data relationships, avoiding data quality deterioration while enabling businesses to adhere to industry regulations and standards. Here are its most popular use cases:
Source and Provenance: demonstrates where data originated and delivers an understanding of source/upstream systems, assets, and processes leading to a particular asset for context, trust, and troubleshooting. For example, a data scientist finds a BI dashboard that they can use to answer a critical business question, but they may not be sure if they can trust the data. By looking at the lineage of the data feeding the BI dashboard, the business user can see that the data comes from an approved data source and can reach out to the data steward if they have more questions.
Impact Analysis and Forecasting: drives business decisions as it maps the progress of data pipelines within a certain environment. It provides an understanding of the dependent/downstream systems, assets, and processes derived from a particular asset for context and determining the effect of potential changes. For example, a data engineer is tasked to add new data into a warehouse which may result in moving columns to another table? What will break? Who should be informed? Data lineage can answer these questions.
Troubleshooting and Root Cause: pinpoints the stage in the data pipeline where an error may have occurred. It allows the understanding of why a downstream dashboard or data mart is behaving unexpectedly or broken by tracing the source of the information and any applicable transformations. For example, a data analyst is skeptical about the data coming from a particular column. With data lineage, the business user can track the logic defined in a data transformation that occurred in an ETL pipeline that generated the data, in order to confirm if the data is accurate.
Risk and Sensitive Data: Assure compliance with industry regulatory frameworks (like GDPR and CCPA) by understanding how sensitive information such as PII is being utilized throughout data pipelines from their sources to reports and dashboards. For example, a data steward needs to track which data sources are providing email.
Metadata management systems featuring data lineage enable teams to achieve a comprehensive view of data relationships. This level of granularity provides transparency and confidence to organizations, ultimately improving governance, impact and root-cause analyses, troubleshooting, and forecasting initiatives.
We took a closer look at data lineage and how it integrates with your enterprise data catalog during our weekly data podcast, Catalog & Cocktails. Special guest Ernie Ostic from our partner, MANTA, joined us for the discussion. Listen to the episode now, and register for Catalog & Cocktails to join us every week.